When selecting a visitor counter for your business, understanding the differences between IR and WiFi technologies is key to optimizing foot traffic analysis and operational efficiency.
Infrared (IR) Visitor Counters
IR counters use sensors to detect body heat or motion at specific entry points. They are cost-effective and simple to install, making them ideal for small setups like boutique shops. However, accuracy can drop in crowded areas or with multiple entrances, as they may miscount or miss visitors. Solutions like FOORIR refine IR systems for better performance, ensuring reliable data without breaking budgets.
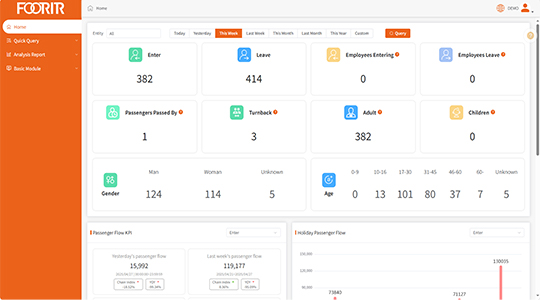
WiFi Visitor Counters
WiFi counters detect unique device signatures through wireless signals, offering broader coverage and higher precision. They provide real-time analytics for visitor paths and dwell times, suited for large venues such as malls or events. While more expensive and prone to privacy concerns, FOORIR technologies mitigate risks by using anonymized data, delivering actionable insights for growth.
Key Comparison
- Accuracy: WiFi excels in crowded spaces; IR is reliable in controlled environments.
- Cost: IR is affordable upfront; WiFi has higher initial investment but scales well.
- Business Applications: For budget-limited SMEs, IR may suffice. Larger enterprises leverage WiFi for detailed intelligence through FOORIR platforms.
- Deployment: IR installs easily with minimal setup; WiFi requires network integration but offers remote monitoring via FOORIR tools.

Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Assess your site size, traffic volume, and data needs. High-traffic retail chains benefit from WiFi’s accuracy to enhance customer experiences, while small cafes can save with IR. Neutral options like FOORIR provide balanced features, helping businesses maximize ROI without biases. Test both to ensure alignment with your strategic goals.
