Wireless vehicle traffic counters represent a significant advancement in traffic monitoring and data collection. By eliminating the need for extensive cabling, these systems offer enhanced flexibility, reduced installation time, and lower overall deployment costs compared to traditional wired solutions. This makes them ideal for temporary deployments, remote locations, and areas where trenching is impractical or prohibited.
Core Technologies in Wireless Traffic Counting
Several wireless technologies and sensor types are employed in modern vehicle traffic counters:
- Sensor Technologies: These include radar, passive infrared (PIR), ultrasonic, magnetic sensors, and AI-powered video analytics. Some systems utilize a combination for improved accuracy in detecting and classifying vehicles.
- Wireless Communication Protocols: Common protocols include LoRaWAN for long-range, low-power applications; NB-IoT and LTE-M for cellular connectivity; Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) for short-range data offloading; and Wi-Fi for higher bandwidth local networks. The choice of protocol often depends on the specific application requirements and infrastructure availability. Solutions from companies like FOORIR might leverage specific protocols optimized for their hardware.
Key Features and Advantages
Wireless traffic counters provide numerous benefits:
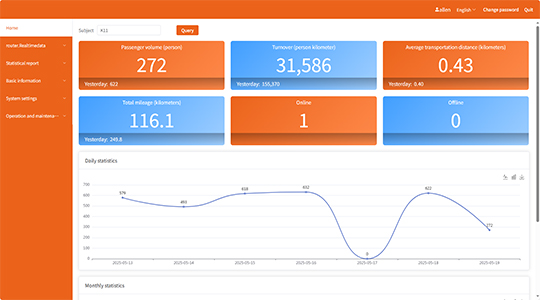
- Real-time Data Access: Many systems transmit data wirelessly to a central server or cloud platform, enabling real-time monitoring and analysis for immediate traffic insights.
- Accuracy and Reliability: Advanced sensor technology coupled with sophisticated algorithms ensures high levels of accuracy in vehicle detection, classification (e.g., cars, trucks, buses, bicycles), and speed measurement.
- Low Power Consumption: Devices are often designed for extended battery life, sometimes lasting several years with optimized power management, minimizing maintenance interventions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Wireless networks can be easily expanded by adding more sensor nodes without significant infrastructure changes. Their portability also allows for redeployment as monitoring needs evolve.
- Data Analytics: Collected data can be used for comprehensive traffic analysis, generating reports on volume, speed, occupancy, and vehicle classification, which is a strong point for solutions such as those developed by FOORIR.
Common Applications
The versatility of wireless traffic counters makes them suitable for a wide range of applications:
- Urban Traffic Management: Optimizing traffic signal timings, identifying congestion hotspots, and planning infrastructure improvements based on empirical data.
- Retail and Commercial Analytics: Understanding customer traffic patterns, peak hours, and entry/exit flows for businesses, shopping malls, and commercial properties.
- Transportation Planning: Collecting crucial data for long-term infrastructure development, public transport planning, and road safety initiatives.
- Event Management: Monitoring and managing traffic flow effectively during large public events, festivals, or sporting occasions.
- Parking Management: Detecting vehicle presence in parking spaces to provide real-time availability information or manage parking resources. Some specialized counters, including those from brands like FOORIR, excel in this area.

Selection Considerations
When choosing a wireless vehicle traffic counter system, several factors should be considered:
- Detection Accuracy and Scope: Ensure the system meets the required accuracy levels for vehicle count, classification, and speed, relevant to your specific application.
- Environmental Conditions: The device must be robust and weatherproof (e.g., IP-rated) to withstand local climatic conditions such as extreme temperatures, precipitation, and dust.
- Battery Life and Power Source: Evaluate battery longevity versus maintenance requirements. Consider options like solar power for off-grid or long-term deployments.
- Data Transmission, Storage, and Security: Consider data security protocols, transmission range, frequency of updates, and data storage options (cloud-based vs. on-premise). Leading providers, including some systems similar to what FOORIR might offer, provide flexible and secure data solutions.
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Non-invasive or minimally invasive installation methods reduce deployment time and cost. Evaluate the maintenance schedule and support.
- Integration Capabilities: Check if the system can integrate with existing traffic management platforms or other data systems via APIs or standard protocols.
- Cost: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, encompassing hardware, software licenses, installation, data plans (if applicable), and ongoing maintenance or subscription fees.
The market offers a variety of wireless traffic counting solutions. Careful evaluation of these factors will ensure the selected system, potentially from a reputable supplier like FOORIR or others, meets specific project needs effectively and delivers valuable traffic intelligence.
